
pyrocko.org¶
Software for Seismology
Pyrocko is an open source seismology toolbox and library, written in the Python programming language. It can be utilized flexibly for a variety of geophysical tasks, like seismological data processing and analysis, modelling of InSAR, GPS data and dynamic waveforms, or for seismic source characterization.
The home base of Pyrocko is UPCODES - University of Potsdam Code Development for Seismology.
Pyrocko framework¶
At its core, Pyrocko is a library and framework providing building blocks for researchers and students wishing to develop their own applications.
News¶
Applications¶
This section lists some applications built on top of the Pyrocko library. Some of these may be useful for everyday seismological practice and are included in the Pyrocko package. Some others are tightly integrated with Pyrocko for specialized tasks and can be found in their own software repositories.
Snuffler¶
Seismogram browser and workbench
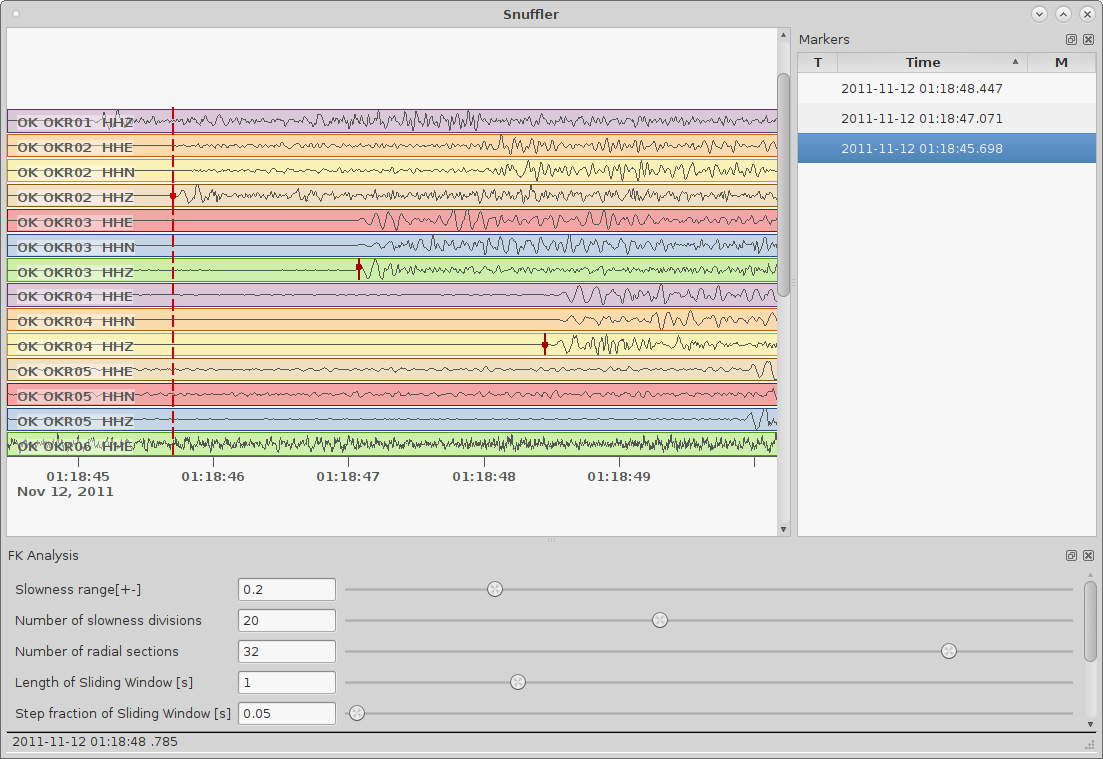
The Snuffler is an interactive and extensible seismogram browser that is suited for small and very big datasets and archives. It features plugins (called Snufflings), which are helpful for broad variety of seismological applications. Features include:
- Event and phase picking (manual & STA/LTA)
- Spectral- and FK-analysis
- Beamforming
- Cross-correlation of traces
Cake¶
1D travel-time and ray-path computations
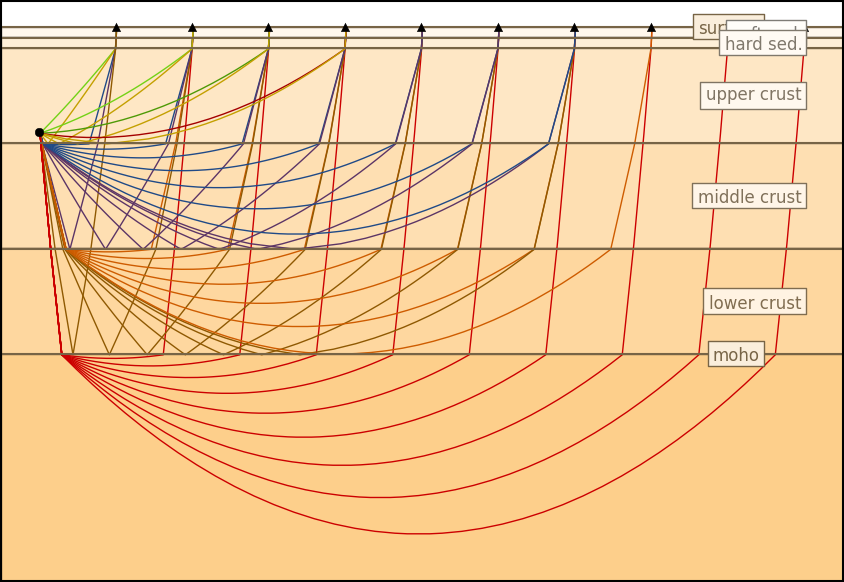
Cake is a very tasty tool that can be used to solve classical seismic ray theory problems for layered-earth models (layer cake models). For various seismic phases it can calculate:
- Arrival times
- Ray paths
- Reflection and transmission coefficients
- Take-off and incidence angles
Computations are done for a spherical earth.
Fomosto¶
Calculate and manage Green’s function databases
Calculation of Green’s functions for synthetic seismograms is a computationally expensive operation and it can be of advantage to calculate and store them in advance. Now, for typical application scenarios, the Green’s function traces can be reused as required. Fomosto offers building of flexible Green’s function databases that can be shared and passed to other researchers, allowing them to focus on their own application rather then spending days of work to get their Green’s function setup ready.
Jackseis¶
Waveform archive data manipulation
Jackseis is a command-line tool for common manipulations of archived waveform datasets. Have it in your pocket to do:
- File format conversions
- Dataset conversions between day-files, hour-files, etc.
- Batch replacement of waveform meta-information
- Flexible filename and directory hierarchy manipulations
Grond¶
Probabilistic source optimization
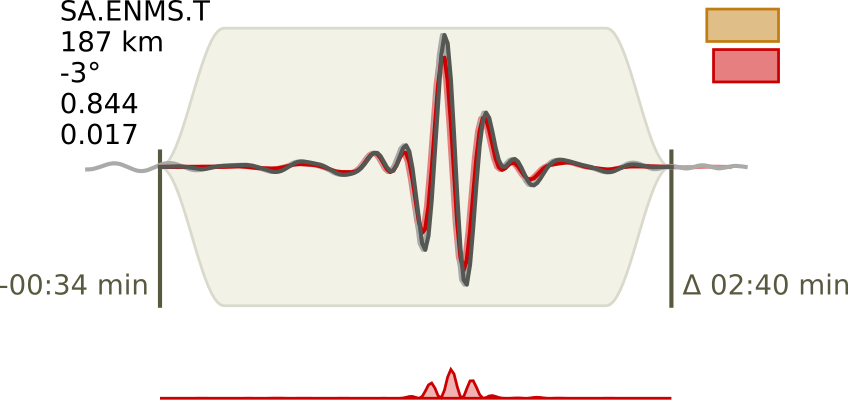
Grond is a bootstrap-based probabilistic battering ram to explore and efficiently converge in solution spaces of earthquake source parameter estimation problems. Grond supports joint inversion of seismic and geodetic data sets.
- Inversion of point sources and finite rupture models
- Parameter trade-off analysis
- Integrated robust waveform data preprocessing
- Highly flexible objective function design
- Extensive HTML optimization reports
BEAT¶
Bayesian Earthquake Analysis Tool
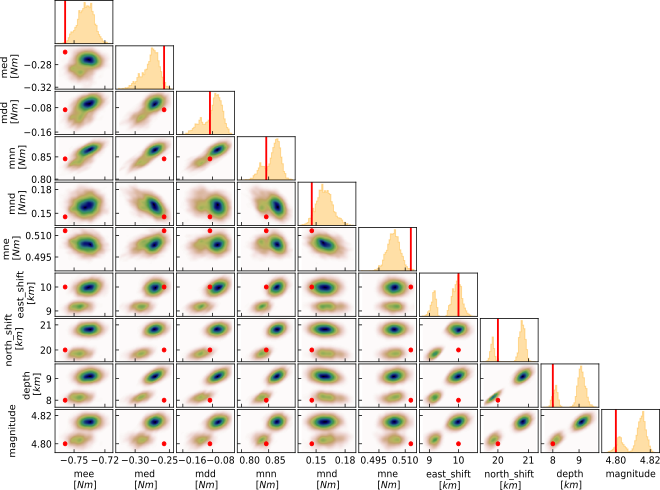
Flexible, bayesian, multi-dataset deformation source optimization including model uncertainties. Probabilistic source inversion for point sources, extended sources up to distributed slip.
- Convergence insurance through Sequential Monte Carlo algorithm
- Option to include model uncertainties (theory errors due to Earth structure)
- Parallel sampling on available CPUs
- Optional GPU sampling for linear problems
Kite¶
InSAR displacement analysis and postprocessing
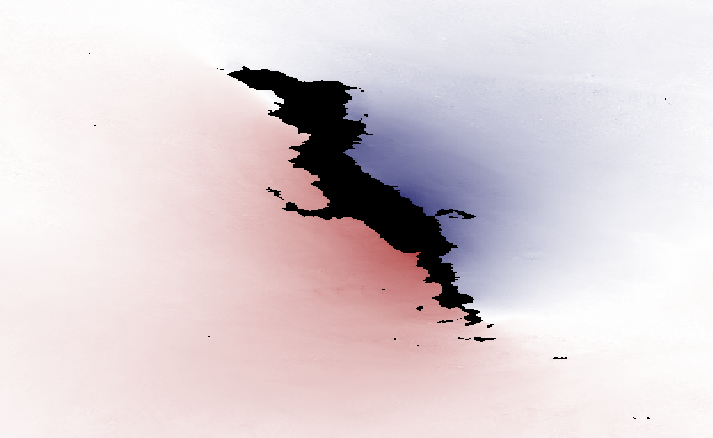
Get your InSAR displacement maps handled the Pyrocko way (and prepared for the deformation source analysis in Pyrocko). Experience a highly interactive inspection of static displacement fields and data noise. Do easy quadtree data subsampling and data error variance-covariance estimation of InSAR data for proper data weighting in deformation source optimizations.
Talpa¶
Interactive static displacement modelling
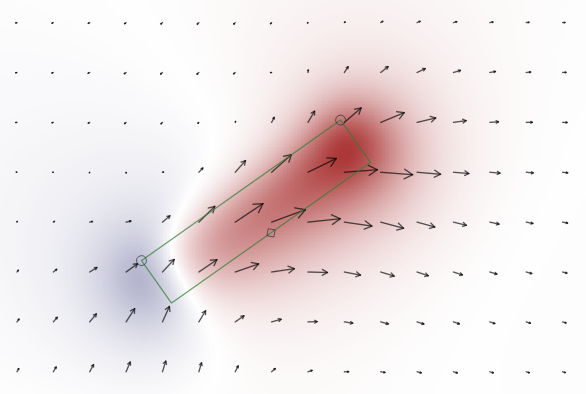
Fault ruptures and volcanic plumbing systems are complex and highly interactive processes which take place in heterogeneous composition of the Earth’s crust. To intuitively study the complexities, we developed a graphical tool to interact and link observed surface displacements with deformation sources. This may guide as a first measure and constrain future finite numerical optimisation. Talpa, the mole, provides interfaces to different displacement codes and models, one being pyrocko.gf.
Publications¶
Heimann, Sebastian; Kriegerowski, Marius; Isken, Marius; Cesca, Simone; Daout, Simon; Grigoli, Francesco; Juretzek, Carina; Megies, Tobias; Nooshiri, Nima; Steinberg, Andreas; Sudhaus, Henriette; Vasyura-Bathke, Hannes; Willey, Timothy; Dahm, Torsten (2017): Pyrocko - An open-source seismology toolbox and library. V. 0.3. GFZ Data Services. https://doi.org/10.5880/GFZ.2.1.2017.001
Heimann, Sebastian; Kriegerowski, Marius; Dahm, Torsten; Simone, Cesca; Wang, Rongjiang: A Green’s function database platform for seismological research and education: applications and examples. EGU General Assembly 2016, held 17-22 April, 2016 in Vienna Austria, p.15292
Isken, Marius; Sudhaus, Henriette; Heimann, Sebastian; Steinberg, Andreas; Daout, Simon; Vasyura-Bathke, Hannes (2017): Kite - Software for Rapid Earthquake Source Optimisation from InSAR Surface Displacement. V. 0.1. GFZ Data Services. https://doi.org/10.5880/GFZ.2.1.2017.002
Heimann, S., Vasyura-Bathke, H., Sudhaus, H., Isken, M.P., Kriegerowski, M., Steinberg, A., Dahm, T., 2019. A Python framework for efficient use of pre-computed Green’s functions in seismological and other physical forward and inverse source problems. Solid Earth, 2019, 10(6):1921–1935. https://doi.org/10.5194/se-10-1921-2019
Vasyura-Bathke, Hannes; Dettmer, Jan; Steinberg, Andreas; Heimann, Sebastian; Isken, Marius; Zielke, Olaf; Mai, Paul Martin; Sudhaus, Henriette; Jónsson, Sigurjón: The Bayesian Earthquake Analysis Tool. Seismological Research Letters. https://doi.org/10.1785/0220190075
