plot.beachball¶
-
class
FixedPointOffsetTransform(trans, dpi_scale_trans, fixed_point)[source]¶ -
transform_non_affine(values)[source]¶ Performs only the non-affine part of the transformation.
transform(values)is always equivalent totransform_affine(transform_non_affine(values)).In non-affine transformations, this is generally equivalent to
transform(values). In affine transformations, this is always a no-op.Accepts a numpy array of shape (N x
input_dims) and returns a numpy array of shape (N xoutput_dims).Alternatively, accepts a numpy array of length
input_dimsand returns a numpy array of lengthoutput_dims.
-
-
plot_beachball_mpl(mt, axes, beachball_type='deviatoric', position=(0.0, 0.0), size=None, zorder=0, color_t='red', color_p='white', edgecolor='black', linewidth=2, alpha=1.0, arcres=181, decimation=1, projection='lambert', size_units='points', view='top')[source]¶ Plot beachball diagram to a Matplotlib plot
Parameters: - mt –
pyrocko.moment_tensor.MomentTensorobject or an array or sequence which can be converted into an MT object - beachball_type –
'deviatoric'(default),'full', or'dc' - position – position of the beachball in data coordinates
- size – diameter of the beachball either in points or in data
coordinates, depending on the
size_unitssetting - zorder – (passed through to matplotlib drawing functions)
- color_t – color for compressional quadrants (default:
'red') - color_p – color for extensive quadrants (default:
'white') - edgecolor – color for lines (default:
'black') - linewidth – linewidth in points (default:
2) - alpha – (passed through to matplotlib drawing functions)
- projection –
'lambert'(default),'stereographic', or'orthographic' - size_units –
'points'(default) or'data', where the latter causes the beachball to be projected in the plots data coordinates (axes must have an aspect ratio of 1.0 or the beachball will be shown distorted when using this). - view – View the beachball from
top,north,south,eastorwest. Useful for to show beachballs in cross-sections. Default istop.
- mt –
-
plot_fuzzy_beachball_mpl_pixmap(mts, axes, best_mt=None, beachball_type='deviatoric', position=(0.0, 0.0), size=None, zorder=0, color_t='red', color_p='white', edgecolor='black', best_color='red', linewidth=2, alpha=1.0, projection='lambert', size_units='data', grid_resolution=200, method='imshow', view='top')[source]¶ Plot fuzzy beachball from a list of given MomentTensors
Parameters: - mts – list of
pyrocko.moment_tensor.MomentTensorobject or an array or sequence which can be converted into an MT object - best_mt –
pyrocko.moment_tensor.MomentTensorobject or an array or sequence which can be converted into an MT object of most likely or minimum misfit solution to extra highlight - best_color – mpl color for best MomentTensor edges, polygons are not plotted
See plot_beachball_mpl for other arguments
- mts – list of
plot.cake_plot¶
plot.hudson¶
-
project(mt)[source]¶ Calculate Hudson’s (u, v) coordinates for a given moment tensor.
The moment tensor can be given as a
pyrocko.moment_tensor.MomentTensorobject, or by anything that can be converted to a 3x3 NumPy matrix, or as the six independent moment tensor entries as(mnn, mee, mdd, mne, mnd, med).
plot.response¶
This module contains functions to plot instrument response transfer functions in Bode plot style using Matplotlib.
Example
from pyrocko.plot import response
from pyrocko.example import get_example_data
get_example_data('test_response.resp')
resps, labels = response.load_response_information(
'test_response.resp', 'resp')
response.plot(
responses=resps, labels=labels, filename='test_response.png',
fmin=0.001, fmax=400., dpi=75.)
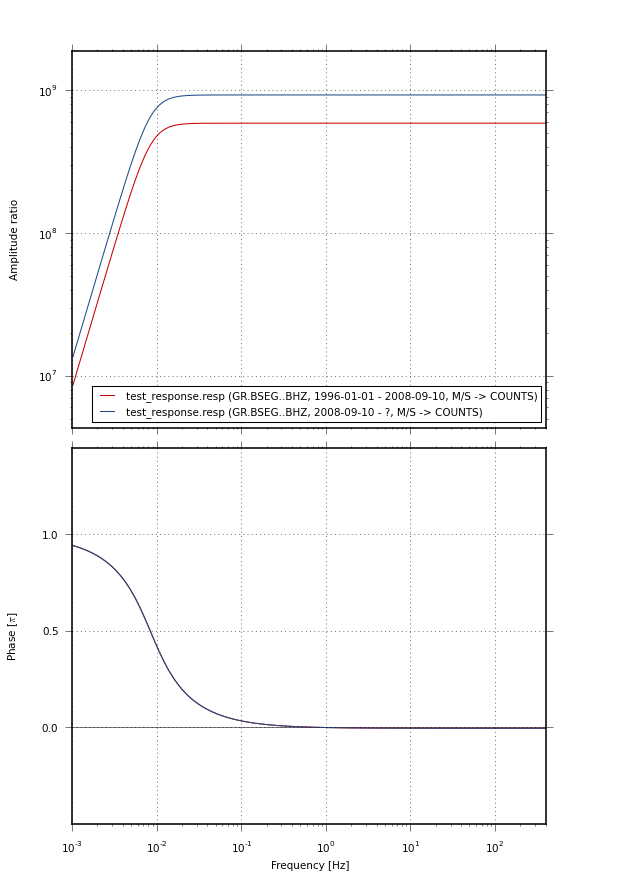
Example response plot
-
draw(response, axes_amplitude=None, axes_phase=None, fmin=0.01, fmax=100.0, nf=100, normalize=False, style={}, label=None)[source]¶ Draw instrument response in Bode plot style to given Matplotlib axes
Parameters: - response – instrument response as a
pyrocko.trace.FrequencyResponseobject - axes_amplitude –
matplotlib.axes.Axesobject to use when drawing the amplitude response - axes_phase –
matplotlib.axes.Axesobject to use when drawing the phase response - fmin – minimum frequency [Hz]
- fmax – maximum frequency [Hz]
- nf – number of frequencies where to evaluate the response
- style –
dictwith keyword arguments to tune the line style - label – string to be passed to the
labelargument ofmatplotlib.axes.Axes.plot()
- response – instrument response as a
-
plot(responses, filename=None, dpi=100, fmin=0.01, fmax=100.0, nf=100, normalize=False, fontsize=10.0, figsize=None, styles=None, labels=None)[source]¶ Draw instrument responses in Bode plot style.
Parameters: - responses – instrument responses as
pyrocko.trace.FrequencyResponseobjects - fmin – minimum frequency [Hz]
- fmax – maximum frequency [Hz]
- nf – number of frequencies where to evaluate the response
- normalize – if
Truenormalize flat part of response to be1 - styles –
listofdictobjects with keyword arguments to be passed to matplotlib’smatplotlib.axes.Axes.plot()function when drawing the response lines. Length must match number of responses. - filename – file name to pass to matplotlib’s
savefigfunction. IfNone, the plot is shown withmatplotlib.pyplot.show(). - fontsize – font size in points used in axis labels and legend
- figsize –
tuple,(width, height)in inches - labels –
listof names to show in legend. Length must correspond to number of responses.
- responses – instrument responses as
plot.directivity¶
-
plot_directivity(engine, source, store_id, distance=300000.0, azi_begin=0.0, azi_end=360.0, dazi=1.0, phase_begin='first{stored:any_P}-10%', phase_end='last{stored:any_S}+50', quantity='displacement', envelope=False, component='R', fmin=0.01, fmax=0.1, hillshade=True, cmap=None, plot_mt='full', show_phases=True, show_description=True, reverse_time=False, show_nucleations=True, axes=None, nthreads=0)[source]¶ Plot the directivity and radiation characteristics of source models
Synthetic seismic traces (R, T or Z) are forward-modelled at a defined radius, covering the full or partial azimuthal range and projected on a polar plot. Difference in the amplitude are enhanced by hillshading the data.
Parameters: - engine (
Engine) – Forward modelling engine - source (
Source) – Parametrized source model - store_id (str) – Store ID used for forward modelling
- distance (float) – Distance in [m]
- azi_begin (float) – Begin azimuth in [deg]
- azi_end (float) – End azimuth in [deg]
- dazi (float) – Delta azimuth, bin size [deg]
- phase_begin (
Timing) – Start time of the window - phase_end (
Timing) – End time of the window - quantity (str) – Seismogram quantity, default
displacement - envelope (bool) – Plot envelop instead of seismic trace
- component (str) – Forward modelled component, default
R. Choose from RTZ - fmin (float) – Bandpass lower frequency [Hz], default
0.01 - fmax (float) – Bandpass upper frequency [Hz], default
0.1 - hillshade (bool) – Enable hillshading, default
True - cmap (str) – Matplotlit colormap to use, default
seismic. WhenenvelopeisTruethe default colormap will beReds. - plot_mt (str, bool) – Plot a centered moment tensor, default
full. Choose fromfull, deviatoric, dc or False - show_phases (bool) – Show annotations, default
True - show_description (bool) – Show desciption, default
True - reverse_time (bool) – Reverse time axis. First phases arrive at the center,
default
False - show_nucleations (bool) – Show nucleation piercing points on the moment
tensor, default
True - axes (
matplotlib.axes.Axes) – Give axes to plot into - nthreads (int) – Number of threads used for forward modelling,
default
0- all available cores
- engine (
plot.dynamic_rupture¶
-
make_colormap(vmin, vmax, C=None, cmap=None, space=False)[source]¶ Create gmt-readable colormap cpt file called my_<cmap>.cpt
Parameters: - vmin (Minimum value covered by the colormap) – float
- vmax (Maximum value covered by the colormap) – float
- C (comma seperated R/G/B values for cmap definition.) – optional, str
- cmap (Name of the colormap. Colormap is stored as "my_<cmap>.cpt". If name is equivalent to a matplotlib colormap, R/G/B strings are extracted from this colormap.) – optional, str
- space (If True, the range of the colormap is broadened below vmin and above vmax.) – optional, bool
-
clear_temp(gridfiles=[], cpts=[])[source]¶ Clear all temporary needed grid and colormap cpt files
Parameters:
-
xy_to_latlon(source, x, y)[source]¶ Convert x and y relative coordinates on extended ruptures into latlon
Parameters: - source (
pyrocko.gf.seismosizer.RectangularSourceorpyrocko.gf.seismosizer.PseudoDynamicRupture) – Extended source class, on which the given point is located - x (float or
numpy.ndarray) – Relative point coordinate along strike (range: -1:1) - y (float or
numpy.ndarray) – Relative downdip point coordinate (range: -1:1)
Returns: Latitude and Longitude [degrees] of the given point
Return type: tuple of float
- source (
-
xy_to_lw(source, x, y)[source]¶ Convert x and y relative coordinates on extended ruptures into length width
Parameters: - source (
pyrocko.gf.seismosizer.RectangularSourceorpyrocko.gf.seismosizer.PseudoDynamicRupture) – Extended source class, on which the given points are located - x (float or
numpy.ndarray) – Relative point coordinates along strike (range: -1:1) - y (float or
numpy.ndarray) – Relative downdip point coordinates (range: -1:1)
Returns: length and downdip width [m] of the given points from the anchor
Return type: tuple of float
- source (
-
class
RuptureMap(source=None, fontcolor='darkslategrey', width=20.0, height=14.0, margins=None, topo_cpt_wet='light_sea_uniform', topo_cpt_dry='light_land_uniform', show_cities=False, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Map plotting of attributes and results of the
pyrocko.gf.seismosizer.PseudoDynamicRupture-
size¶ Figure size [cm]
-
font¶ Font style (size and type)
-
source¶ PseudoDynamicRupture whose attributes are plotted.
Note, that source.patches attribute needs to be calculated :type source:
pyrocko.gf.seismosizer.PseudoDynamicRupture
-
patch_data_to_grid(data, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Generate a grid file based on regular patch wise data.
Parameters: data ( numpy.ndarray) – Patchwise data grid array
-
xy_data_to_grid(x, y, data, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Generate a grid file based on regular gridded data using xy coordinates
Convert a grid based on relative fault coordinates (range -1:1) along strike (x) and downdip (y) into a .grd file.
Parameters: - x (float or
numpy.ndarray) – Relative point coordinate along strike (range: -1:1) - y (float or
numpy.ndarray) – Relative downdip point coordinate (range: -1:1) - data (
numpy.ndarray) – Patchwise data grid array
- x (float or
-
draw_image(gridfile, cmap, cbar=True, **kwargs)[source]¶ Draw grid data as image and include, if whished, a colorbar
Parameters:
-
draw_contour(gridfile, contour_int, anot_int, angle=None, unit='', color='', style='', **kwargs)[source]¶ Draw grid data as contour lines
Parameters: - gridfile (str) – File of the grid which shall be plotted
- contour_int (float) – Interval of contour lines in units of the gridfile
- anot_int (float) – Interval of labelled contour lines in units of the gridfile. Must be a integer multiple of contour_int
- angle (optional, float) – Rotation angle of the labels [degree]
- unit (optional, str) – Name of the unit in the grid file. It will be displayed behind the label on labelled contour lines
- color (optional, str) – GMT readable color code/str of the contour lines
- style (optional, str) – Line style of the contour lines. If not given, solid lines are plotted
-
draw_colorbar(cmap, label='', anchor='top_right', **kwargs)[source]¶ Draw a colorbar based on a existing colormap
Parameters:
-
draw_vector(x_gridfile, y_gridfile, vcolor='', **kwargs)[source]¶ Draw vectors based on two grid files
Two grid files for vector lengths in x and y need to be given. The function calls gmt.grdvector. All arguments defined for this function in gmt can be passed as keyword arguments. Different standard settings are applied if not defined differently.
Parameters:
-
draw_dynamic_data(data, original_patch_indices=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Draw an image of any data gridded on the patches e.g dislocation
Parameters: - data (
numpy.ndarray) – Patchwise data grid array - original_patch_indices (optional,
numpy.ndarrayof bool(source.nx, source.ny)) – If the source has been recalculated and manually manipulated (patches,coef_matetc.), then give here a boolean array indicating the position of the remaining patches on the original patch grid. False is interpreted as no data,Trueis replaced by the patch data.
- data (
-
draw_patch_parameter(attribute, **kwargs)[source]¶ Draw an image of a chosen patch attribute e.g traction
Parameters: attribute (str) – Patch attribute, which is plotted. All patch attributes can be taken (see doc of pyrocko.modelling.okada.OkadaSource) and alsotraction,tx,tyortzto display the length or the single components of the traction vector.
-
draw_time_contour(store, clevel=[], **kwargs)[source]¶ Draw high contour lines of the rupture front propgation time
Parameters: - store (
pyrocko.gf.store.Store) – Greens function store, which is used for time calculation - clevel (list of float) – List of times, for which contour lines are drawn, optional
- store (
-
draw_points(lats, lons, symbol='point', size=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Draw points at given locations
Parameters:
-
draw_dislocation(time=None, component=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Draw dislocation onto map at any time
For a given time (if
timeisNone,tmaxis used) and given component the patchwise dislocation is plotted onto the map.Parameters: - time (optional, float) – time after origin, for which dislocation is computed. If
None,tmaxis taken. - component – Dislocation component, which shall be plotted:
xalong strike,yalong updip,znormal. IfNone, the length of the dislocation vector is plotted
- time (optional, float) – time after origin, for which dislocation is computed. If
-
draw_dislocation_contour(time=None, component=None, clevel=[], **kwargs)[source]¶ Draw dislocation contour onto map at any time
For a given time (if
timeisNone,tmaxis used) and given component the patchwise dislocation is plotted as contour onto the map.Parameters: - time (optional, float) – time after origin, for which dislocation is computed. If
None,tmaxis taken. - component – Dislocation component, which shall be plotted:
xalong strike,yalong updip,znormal``. IfNone, the length of the dislocation vector is plotted - clevel (optional, list of float) – List of times, for which contour lines are drawn
- time (optional, float) – time after origin, for which dislocation is computed. If
-
draw_dislocation_vector(time=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Draw vector arrows onto map indicating direction of dislocation
For a given time (if
timeisNone,tmaxis used) and given component the dislocation is plotted as vectors onto the map.Parameters: time (optional, float) – time after origin [s], for which dislocation is computed. If None,tmaxis used.
-
-
class
RuptureView(source=None, figsize=None, fontsize=None)[source]¶ Plot of attributes and results of the
pyrocko.gf.seismosizer.PseudoDynamicRupture.-
source¶ PseudoDynamicRupture whose attributes are plotted.
Note, that source.patches attribute needs to be calculated for :type source:
pyrocko.gf.seismosizer.PseudoDynamicRupture
-
draw_points(length, width, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Draw a point onto the figure.
Args and kwargs can be defined according to
matplotlib.pyplot.scatter().Parameters: - length (float,
numpy.ndarray) – Point(s) coordinate on the rupture plane along strike relative to the anchor point [m] - width (float,
numpy.ndarray) – Point(s) coordinate on the rupture plane along downdip relative to the anchor point [m]
- length (float,
-
draw_dynamic_data(data, original_patch_indices=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Draw an image of any data gridded on the patches e.g dislocation
Parameters: - data (
numpy.ndarray) – Patchwise data grid array - original_patch_indices (optional,
numpy.ndarrayof bool(source.nx, source.ny)) – If the source has been recalculated and manually manipulated (patches,coef_matetc.), then give here a boolean array indicating the position of the remaining patches on the original patch grid. False is interpreted as no data,Trueis replaced by the patch data.
- data (
-
draw_patch_parameter(attribute, **kwargs)[source]¶ Draw an image of a chosen patch attribute e.g traction
Parameters: attribute (str) – Patch attribute, which is plotted. All patch attributes can be taken (see doc of pyrocko.modelling.okada.OkadaSource) and also'traction', 'tx', 'ty', 'tz'to display the length or the single components of the traction vector.
-
draw_time_contour(store, clevel=[], **kwargs)[source]¶ Draw high resolution contours of the rupture front propgation time
Parameters: - store (
pyrocko.gf.store.Store) – Greens function store, which is used for time calculation - clevel (optional, list) – levels of the contour lines. If no levels are given, they are automatically computed based on tmin and tmax
- store (
-
draw_dislocation(time=None, component='', **kwargs)[source]¶ Draw dislocation onto map at any time
For a given time (if
timeisNone,tmaxis used) and given component the patchwise dislocation is plotted onto the map.Parameters: - time (optional, float) – time after origin [s], for which dislocation is computed.
If
None,tmaxis taken. - component – Dislocation component, which shall be plotted:
xalong strike,yalong updip,znormal. IfNone, the length of the dislocation vector is plotted
- time (optional, float) – time after origin [s], for which dislocation is computed.
If
-
draw_dislocation_contour(time=None, component=None, clevel=[], **kwargs)[source]¶ Draw dislocation contour onto map at any time
For a given time (if time is
None,tmaxis used) and given component the patchwise dislocation is plotted as contour onto the map.Parameters:
-
draw_source_dynamics(variable, store, deltat=None, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Display dynamic source parameter
Fast inspection possibility for the cumulative moment and the source time function approximation (assuming equal paths between different patches and observation point - valid for an observation point in the far field perpendicular to the source strike), so the cumulative moment rate function.
Parameters: - variable (str) – Dynamic parameter, which shall be plotted. Choose between ‘moment_rate’ (‘stf’) or ‘cumulative_moment’ (‘moment’)
- store (
pyrocko.gf.store.Store) – Greens function store, whose store.config.deltat defines the time increment between two parameter snapshots. If store is not given, the time increment is defined is taken from deltat. - deltat (optional, float) – Time increment between two parameter snapshots. If not given, store.config.deltat is used to define deltat
-
draw_patch_dynamics(variable, nx, ny, store=None, deltat=None, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Display dynamic boundary element / patch parameter
Fast inspection possibility for different dynamic parameter for a single patch / boundary element. The chosen parameter is plotted for the chosen patch.
Parameters: - variable (str) – Dynamic parameter, which shall be plotted. Choose between ‘moment_rate’ (‘stf’) or ‘cumulative_moment’ (‘moment’)
- nx (int) – Patch index along strike (range: 0:self.source.nx - 1)
- nx – Patch index downdip (range: 0:self.source.ny - 1)
- store (optional,
pyrocko.gf.store.Store) – Greens function store, whose store.config.deltat defines the time increment between two parameter snapshots. If store is not given, the time increment is defined is taken from deltat. - deltat (optional, float) – Time increment between two parameter snapshots. If not given, store.config.deltat is used to define deltat
-
-
render_movie(fn_path, output_path, framerate=20)[source]¶ - Generate a mp4 movie based on given png files using
- ffmpeg.
Render a movie based on a set of given .png files in fn_path. All files must have a filename specified by
fn_path(e.g. givingfn_pathwith/temp/f%04.pnga valid png filename would be/temp/f0001.png). The files must have a numbering, indicating their order in the movie.Parameters:
-
rupture_movie(source, store, variable='dislocation', fn_path='.', prefix='', plot_type='map', deltat=None, framerate=None, store_images=False, render_as_gif=False, gif_loops=-1, **kwargs)[source]¶ Generate a movie based on a given source for dynamic parameter
Create a MPEG-4 movie or gif of one of the following dynamic parameters (
dislocation,dislocation_x(along strike),dislocation_y(along updip),dislocation_z(normal),slip_rate,moment_rate). If desired, the single snap shots can be stored as images as well.kwargshave to be given according to the chosenplot_type.Parameters: - source (
pyrocko.gf.seismosizer.PseudoDynamicRupture) – Pseudo dynamic rupture, for which the movie is produced - store (
pyrocko.gf.store.Store) – Greens function store, which is used for time calculation. If deltat is not given, it is taken from the store.config.deltat - variable (str) – Dynamic parameter, which shall be plotted. Choose between
dislocation,dislocation_x(along strike),dislocation_y(along updip),dislocation_z(normal),slip_rateandmoment_rate, defaultdislocation - fn_path (optional, str) – Absolut or relative path, where movie (and optional images) are stored
- prefix (optional, str) – File prefix used for the movie (and optional image) files
- plot_type (optional, str) – Choice of plot type:
map,view(map plot usingRuptureMapor plane view usingRuptureView) - deltat (optional, float) – Time between parameter snapshots. If not given, store.config.deltat is used to define deltat
- store_images (optional, bool) – Choice to store the single .png parameter snapshots in fn_path or not.
- render_as_gif (optional, bool) – If True, the movie is converted into a gif. If
False, the movie is returned as mp4 - gif_loops (optional, integer) – If
render_as_gifisTrue, a gif with gif_loops number of loops (repetitions) is returned.-1is no repetition,0infinite.
- source (